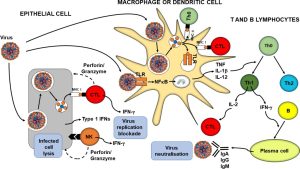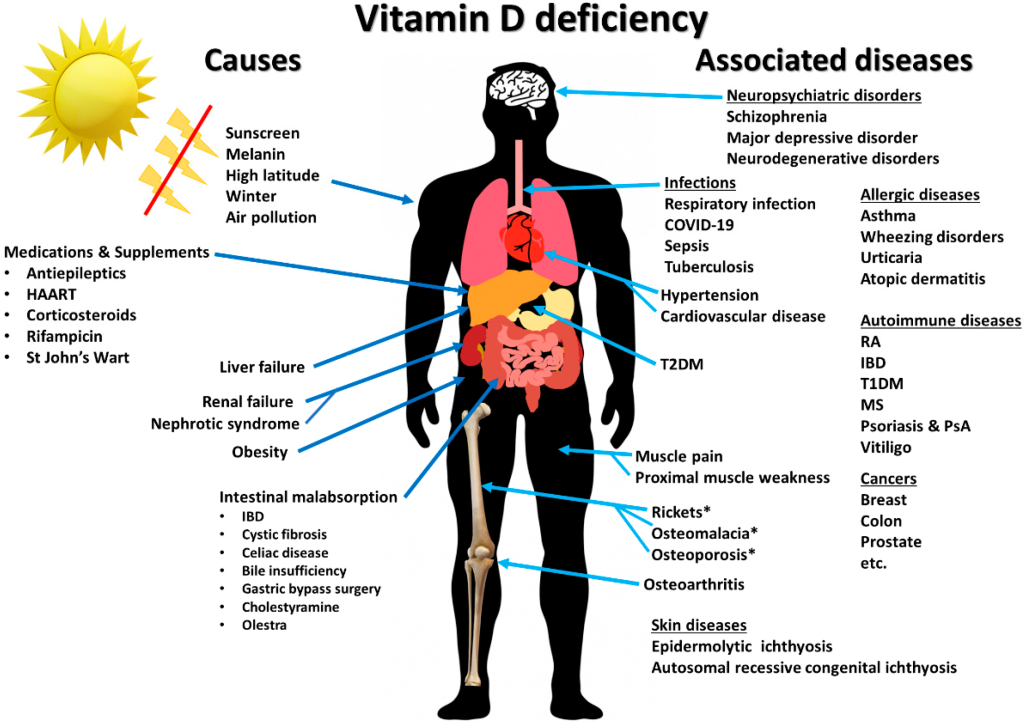
Micronutrients are essential components of a healthy diet that are required in small amounts to maintain optimal health and wellness
However, micronutrient deficiencies are prevalent worldwide and can have significant health consequences. In this article, we will discuss the impact of micronutrient deficiencies on human health
One of the most common micronutrient deficiencies is iron deficiency. Iron is necessary for the production of hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. Iron deficiency can lead to anemia, a condition characterized by fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Severe iron deficiency can also lead to developmental delays in children.
Another essential micronutrient is vitamin A, which is necessary for vision, immune function, and skin health. Vitamin A deficiency can lead to a range of health problems, including night blindness, impaired immune function, and increased susceptibility to infectious diseases. In pregnant women, vitamin A deficiency can also increase the risk of maternal mortality and infant morbidity.
Iodine is another critical micronutrient that is essential for thyroid hormone production. Iodine deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism, a condition characterized by fatigue, weight gain, and depression. In severe cases, iodine deficiency can lead to goiter, an enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Micronutrient deficiencies can also have significant impacts on child development. For example, zinc deficiency can lead to stunted growth and impaired cognitive development. Additionally, deficiencies in folic acid, iron, and iodine during pregnancy can increase the risk of congenital disabilities and infant mortality.
While micronutrient deficiencies are prevalent in many parts of the world, they can also occur in developed countries, particularly among vulnerable populations such as low-income individuals and the elderly. Inadequate intake of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can lead to micronutrient deficiencies, even in those who consume adequate calories.
In conclusion, micronutrient deficiencies can have significant impacts on human health, from anemia and impaired immune function to developmental delays and congenital disabilities. To prevent micronutrient deficiencies, it is essential to consume a balanced and varied diet that includes a wide variety of nutrient-dense foods. Additionally, targeted supplementation may be necessary in cases where dietary intake is inadequate or for vulnerable populations at risk of deficiencies. By prioritizing adequate micronutrient intake, we can improve health outcomes and reduce the burden of micronutrient deficiency-related health problems worldwide.