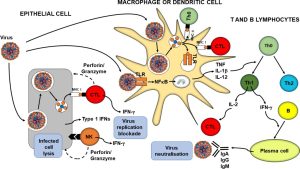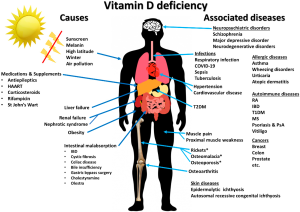
Micronutrient supplements, such as multivitamins, are becoming increasingly popular as a way to boost nutrient intake and promote health
While they can be beneficial in certain situations, there are both pros and cons to incorporating micronutrient supplements into your diet. In this article, we will explore the potential benefits and drawbacks of using micronutrient supplements
Pros:
1. Convenient and Time-Saving: One of the biggest advantages of micronutrient supplements is their convenience. They are easy to take and can be incorporated into your daily routine without much effort. This can be particularly helpful for individuals who are busy and may not have the time to prepare nutrient-dense meals.
2. Nutrient Insurance: Micronutrient supplements can help to ensure that you are meeting your daily nutrient requirements, especially if you have a restrictive diet or have difficulty consuming certain foods due to allergies or intolerances.
3. Targeted Nutrient Support: Some micronutrient supplements are formulated to target specific health concerns or deficiencies, such as iron deficiency or bone health. This can be beneficial for individuals who may have specific nutritional needs or health concerns.
Cons:
1. Cost: Micronutrient supplements can be expensive, especially if you are taking multiple supplements or high-dose supplements. This cost can add up over time, making it difficult for some individuals to afford them.
2. Risk of Overdose: While it may seem like more is better when it comes to micronutrients, consuming too much of certain vitamins and minerals can be harmful. Overdosing on certain vitamins and minerals can lead to toxicity and negative health effects.
3. Lack of Regulation: Unlike medications, micronutrient supplements are not regulated by the FDA in the same way. This means that there may be inconsistencies in the quality and efficacy of different supplements, making it difficult for consumers to know which ones to choose.
4. Not a Substitute for a Healthy Diet: While micronutrient supplements can help to fill nutrient gaps, they should not be used as a substitute for a healthy diet. Whole foods contain a variety of other beneficial compounds, such as fiber and phytochemicals, that are not found in supplements.
In conclusion, micronutrient supplements can be a convenient way to boost nutrient intake and support overall health. However, they are not without their drawbacks, including cost, the risk of overdose, and lack of regulation. It is important to weigh the pros and cons before deciding whether to incorporate micronutrient supplements into your diet, and to remember that they should not be used as a substitute for a healthy diet. Consulting with a healthcare professional can also be helpful in determining if micronutrient supplements are right for you.