Risk Factors and Screening for Early Detection of Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer is the mons Common Cancer Disease Among Women, Affecting 1 in 9 Women Each Year. Severe are the consequence if Detected Late, and TODAY IT is the Leading Cause of Cancer Death Among Women.
Breast Cancer Origintes from Cells Produced Uncontrollably by The Mammary Glands. AS These Cells Develop, they can spread to Neighboring Areas. Invasive carcinoma presents spread and infiltration of tumor cells into surrounding tissues (metastasis); in situ carcinoma presents tumor cells only within the lobules and mammary ducts.
The Most Common Types of Breast Cancer Involve Cells in the Lobules (Connected to the Mammary Glands), or Milk Ducts (Most Common Type Involving 70% of Cancer Cases)
Risk factors related to the development of this tumor:
- Family: Having Cases of Breast or Ovarian Cancer in the Family Can Incasse The ’ Incident of this Disease;
- AGE: IT is Believed That with Advancing Years, The Risk of Developing Breast Cancer Incaases. It has been estimated, However, that 60 percent of casees affects women Younger than 55;
- Genetic mutation: Women with an ’ Abnormality in the BRCA Genes (Associated with the Development of Breast or Ovarian Cancer) are More At Risk of Developing a Similar Cancer.
Early Diagnosis Is Most IMPORTANT. If Breast Cancer IS Detected When it is in Situ (zero internship), The 5-Year Survival Rate from Diagnosis for Patient Reaches 98% 3 .
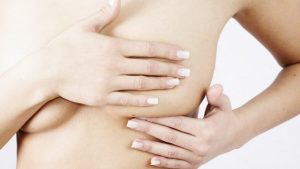
A prevention strategy can be implemented after having a breast screening. Self-palpation is useful to detect nodules, secretions or other abnormalities. Important is to combine checkups with a breast specialist.
Genetic test that is able to detect BRCA gene mutations is useful for early diagnosis. A saliva or blood sample is needed from which DNA is studied to detect abnormalities in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes 4 .
Ultrasound is a screening exam that scans breast tissue for lumps or cysts with fluid. Mammography (extremely reliable examination) detects many types of cancer in the early stages, when they cannot yet be detected by palpation.